RPA is like having a virtual workforce that handles the routine so your human workforce can handle the exceptional.
Have you ever wished you could clone yourself to handle all those boring, repetitive tasks at work? That’s essentially what Robotic Process Automation (RPA) does for businesses. But don’t worry – we’re not talking about physical robots walking around your office. Let’s break down what RPA really means in plain English.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
- What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is like having a digital assistant that can take over the routine, repetitive tasks that humans typically handle. Imagine software robots (or “bots”) that can click buttons, type information, copy and paste data, and move files around – just like you would, but without needing coffee breaks!
These digital workers follow specific rules to complete tasks exactly as instructed, working tirelessly 24/7 without complaining about doing the same thing over and over again.
In simple terms, RPA is technology that allows anyone to configure computer software to mimic human actions to perform business processes. Think of it as teaching a computer program to do the mundane parts of your job so you can focus on more meaningful work.
What is RPA in Simple Terms?
If your eyes glaze over when hearing technical definitions, here’s RPA explained through everyday examples:
- The Digital Assistant: RPA is like having a super-reliable assistant who follows your instructions precisely, never gets tired, and works around the clock.
- The Copy-Paste Master: Remember when you had to copy data from one system and paste it into another? RPA bots excel at this, transferring information between applications without making typos.
- The Form Filler: Those tedious online forms that need filling out repeatedly? RPA can handle that in seconds rather than minutes.
- The Data Organizer: RPA can gather information from various sources, organize it logically, and present it in a useful format.
- The Rule Follower: If a process follows clear rules (“If this happens, then do that”), RPA can follow those rules perfectly every time.
How Does RPA Work?
Understanding how RPA works doesn’t require a technical background. At its core, RPA uses software robots that interact with computer systems the same way humans do – through the user interface.
The Basic Steps of RPA:
- Observe: First, the RPA tool watches and records as a human performs tasks on their computer.
- Learn: The software creates a map of the process, noting which buttons are clicked, what information is entered, and what decisions are made.
- Automate: The RPA bot then replicates these actions, following the same steps as the human would.
- Execute: The bot carries out the process whenever needed – on schedule, when triggered by certain events, or on demand.
Think of it as recording a macro in Excel, but much more sophisticated and able to work across multiple applications and systems.
Types of RPA Bots
Not all RPA bots are created equal. There are three main types:
1. Attended RPA
These bots work alongside humans, like helpful sidekicks. They’re typically triggered by a human and help with specific tasks within a larger process. For example, a customer service representative might use an attended bot to quickly pull up customer information from multiple systems while on a call.
2. Unattended RPA
These are the true workhorses of automation. Unattended bots run independently in the background, often on servers or virtual machines, completing high-volume, routine processes without human intervention. They can be scheduled to run at specific times (like processing invoices every night) or triggered by certain events (like a new form submission).
3. Hybrid RPA
As the name suggests, hybrid RPA combines both attended and unattended capabilities. These sophisticated bots can work independently but may call for human judgment when needed, creating a seamless collaboration between digital and human workers.
RPA vs. AI: Understanding the Difference
People often confuse RPA with Artificial Intelligence (AI), but they’re actually quite different:
|
Feature |
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|
Primary Function |
Follows rules to automate routine tasks |
Simulates human intelligence and learning |
|
Decision Making |
Based on pre-defined rules |
Can make decisions based on patterns and learning |
|
Data Requirements |
Works with structured data |
Can work with both structured and unstructured data |
|
Adaptability |
Limited to programmed scenarios |
Can adapt to new situations |
|
Best For |
Repetitive, rule-based processes |
Complex decisions requiring judgment |
|
Learning Capability |
Does not learn from experiences |
Learns and improves over time |
Think of RPA as the hardworking rule-follower, while AI is the creative problem-solver. While RPA precisely follows instructions, AI can “think” and adapt to new situations.
RPA and Intelligent Automation: The Next Evolution
When RPA is combined with AI technologies, we get what’s called intelligent automation or cognitive automation. This powerful combination takes automation to the next level.
While traditional RPA is fantastic for structured, rules-based processes, intelligent automation can handle more complex scenarios that require some level of judgment or decision-making.
For example:
- Standard RPA: Extracting customer information from a form that always has the same format
- Intelligent Automation: Reading and processing information from invoices with different formats, understanding the content through AI capabilities
Intelligent automation incorporates technologies like:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand and process human language
- Machine Learning to recognize patterns and improve over time
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to read text from images or scanned documents
- Computer Vision to interpret visual information
This evolution from simple RPA to intelligent automation represents the future of business process automation, allowing companies to automate increasingly complex tasks.
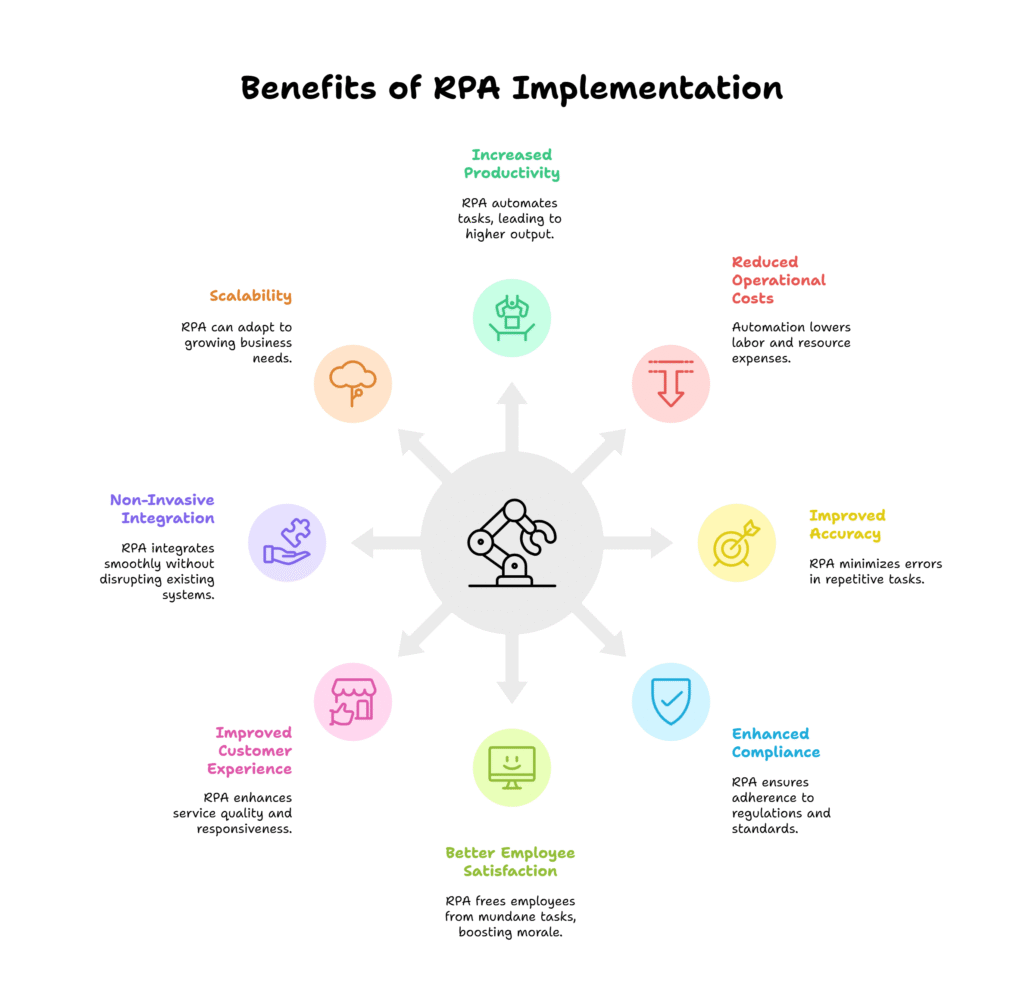
The Benefits of RPA
Implementing RPA can transform how businesses operate, offering numerous advantages beyond simple efficiency. Let’s explore the key benefits:
1. Increased Productivity
RPA bots work tirelessly 24/7/365, processing transactions at lightning speed. What might take a human minutes can take a bot seconds, dramatically increasing throughput. Many companies report productivity gains of 50-70% for automated processes.
2. Reduced Operational Costs
According to various industry studies, RPA can reduce operational costs by 25-50%. Since a single bot can do the work of multiple full-time employees for repetitive tasks, companies can achieve significant cost savings.
3. Improved Accuracy
We all make mistakes, especially when performing repetitive, monotonous tasks. RPA bots, however, follow instructions precisely every time, eliminating human errors like typos or calculation mistakes. This accuracy is especially valuable in industries like banking, insurance, and healthcare, where errors can have serious consequences.
4. Enhanced Compliance
Industries with strict regulatory requirements benefit tremendously from RPA. Bots follow rules perfectly and maintain detailed logs of all actions taken, creating an audit trail that helps demonstrate compliance with regulations.
5. Better Employee Satisfaction
Contrary to fears about automation taking jobs, many organizations find that RPA actually improves employee engagement. By eliminating the mind-numbing aspects of jobs, employees can focus on more meaningful work that requires human skills like creativity, empathy, and problem-solving.
6. Improved Customer Experience
With faster processing times and fewer errors, customers receive better service. For example, loan applications that once took days might be processed in hours, insurance claims can be settled faster, and customer inquiries can receive immediate responses.
7. Non-Invasive Integration
Unlike many IT initiatives that require deep system changes, RPA works with existing systems through the user interface. This makes it relatively quick to implement without disrupting core systems.
8. Scalability
Need to process twice as many invoices this month? Simply deploy more bots. RPA allows businesses to scale operations up or down quickly without the lengthy process of hiring and training new staff.
Challenges of RPA Implementation
While the benefits are compelling, implementing RPA isn’t without challenges. Being aware of these potential hurdles can help organizations prepare effectively:
1. Process Selection and Standardization
Not all processes are suitable for RPA. Processes must be rules-based, stable, and well-documented. Many organizations struggle to identify the right candidates for automation or try to automate processes that are actually broken or inefficient.
2. Managing Expectations
Some companies expect RPA to be a magic solution that transforms their business overnight. In reality, successful implementation requires careful planning, process analysis, and ongoing management.
3. Change Management
Employees may resist automation due to fear of job losses or significant changes to their roles. Effective change management and clear communication about how RPA will impact the workforce are essential.
4. Maintenance Requirements
Business processes change, and systems get updated. RPA bots need regular maintenance to ensure they continue working correctly when the underlying applications or rules change.
5. Security and Governance
RPA bots often need access to sensitive systems and data. Establishing proper security protocols, access controls, and governance frameworks is crucial but can be complex.
6. Scaling Beyond Pilots
Many organizations successfully implement small RPA pilots but struggle when trying to scale to enterprise-wide automation. Building a proper Center of Excellence (CoE) and automation operating model is key to successful scaling.
7. RPA Data Dependency
Bots can only work with the data they’re given. Poor data quality or unexpected data formats can cause RPA processes to fail or produce incorrect results.
RPA Use Cases Across Industries
One of the best ways to understand RPA’s potential is to explore how it’s being used across different industries. Here are some practical applications:
RPA in Banking and Finance
Banks and financial institutions were early adopters of RPA technology, using it for:
- Account opening and KYC processing: Automating customer verification and documentation
- Loan processing: Gathering credit information, validating data, and preparing reports
- Fraud detection: Monitoring transactions for suspicious patterns
- Regulatory reporting: Compiling and submitting required reports to regulatory bodies
- Invoice processing: Matching purchase orders with invoices and receipts
For example, a major bank implemented RPA for its account closure process, reducing processing time from 30 minutes to just 2 minutes per account while ensuring 100% compliance with regulations.
RPA in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use RPA to improve patient care and operational efficiency:
- Patient scheduling and registration: Managing appointments and gathering patient information
- Claims processing: Verifying insurance eligibility and processing claims
- Medical billing: Generating and sending bills, tracking payments
- Healthcare records management: Ensuring patient records are updated across systems
- Inventory management: Tracking medical supplies and generating orders when needed
A healthcare provider implemented RPA for insurance verification, reducing the process from 15 minutes to just 5 seconds per patient while improving accuracy from 80% to 99%.
RPA in Insurance
Insurance companies leverage RPA for:
- Claims processing: Verifying claims data and fast-tracking simple claims
- Policy administration: Managing policy issuance, renewals, and cancellations
- Underwriting support: Gathering and validating information for risk assessment
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations
- Customer service: Providing quick responses to common customer inquiries
One insurance company automated its claims processing, reducing handling time by 75% and improving customer satisfaction scores by 15%.
RPA in Retail
Retailers use RPA to stay competitive in a fast-moving industry:
- Inventory management: Tracking stock levels and automating reorders
- Price comparison: Monitoring competitor pricing
- Order processing: Managing orders from receipt to fulfillment
- Returns processing: Handling customer returns and refunds
- Supply chain management: Coordinating with suppliers and tracking shipments
A major retailer implemented RPA for inventory management, reducing out-of-stock incidents by 30% and improving inventory accuracy to 99%.
RPA in Human Resources
HR departments across industries use RPA for:
- Employee onboarding: Setting up new employees in multiple systems
- Payroll processing: Calculating wages, taxes, and benefits
- Time and attendance tracking: Recording employee hours and absences
- Benefits administration: Managing employee benefits enrollment and changes
- HR reporting: Generating reports on workforce metrics
A large corporation automated its employee onboarding process with RPA, reducing processing time from 3 days to just 4 hours while ensuring 100% accuracy in system setups.
RPA in IT Operations
IT departments leverage RPA to automate their own processes:
- System monitoring: Checking system health and alerting on issues
- User account management: Creating, modifying, and deactivating user accounts
- Backup and recovery: Managing routine backup processes
- Patch management: Deploying software updates across systems
- Help desk operations: Resolving common user issues
A technology company implemented RPA for its helpdesk, automatically resolving 40% of common issues without human intervention, reducing average resolution time from hours to minutes.
Is Your Task Right for RPA?
Not every business task is right for RPA. Here is how you can tell if a task is good for automation:
Good Candidates for RPA:
- Rule-based processes: Processes with clear, definable rules
- High-volume activities: Tasks performed frequently or in large numbers
- Stable and mature processes: Well-established processes that don’t change often
- Structured digital inputs: Processes that use data in standard formats
- Low exception rates: Tasks that rarely require human judgment for special cases
- High manual effort: Processes that consume significant employee time
- Prone to human error: Tasks where mistakes are common and costly
Poor Candidates for RPA:
- Processes requiring judgment: Tasks needing human decision-making or creativity
- Unstable or changing processes: Procedures that frequently change
- Processes with many exceptions: Tasks with numerous special cases
- Unstructured inputs: Processes dealing with freeform text or varied formats
- Low-volume activities: Tasks performed infrequently
- Processes requiring physical handling: Tasks involving physical objects
To determine if a process is suitable for RPA, ask these questions:
- Can you clearly define the rules for this process?
- Is the process stable and unlikely to change frequently?
- Does the process involve digital systems rather than paper or physical items?
- Is the process repetitive and time-consuming?
- Does the process follow the same steps each time with few exceptions?
If you answered “yes” to most of these questions, the process might be a good candidate for RPA.
How to Use RPA in the Right Way
Implementing RPA requires thoughtful planning and execution. Here’s a roadmap for success:
1. Define Your Automation Strategy
Before diving into implementation, establish clear goals for your RPA program. Are you primarily focused on cost reduction, improving accuracy, enhancing customer experience, or freeing up employee time? Your objectives will guide your implementation approach.
2. Select the Right Processes
Conduct a thorough process assessment to identify suitable candidates for automation. Look for high-volume, rules-based processes with measurable outcomes. Consider starting with simpler processes to build confidence and experience.
3. Choose the Right RPA Tools
Several RPA vendors offer solutions with different strengths:
- UiPath: Known for its user-friendly interface and strong community support
- Automation Anywhere: Offers robust analytics and scalability
- Blue Prism: Emphasizes security and governance
- Microsoft Power Automate: Integrates seamlessly with Microsoft products
- Pegasystems: Combines RPA with business process management
Select a tool that aligns with your specific needs, technical environment, and long-term automation goals.
4. Build Your Automation Team
Successful RPA implementation requires the right skills and organizational structure. Consider establishing:
- Center of Excellence (CoE): A central team that develops standards, provides governance, and shares best practices
- Process analysts: Subject matter experts who understand the processes being automated
- RPA developers: Technical specialists who build and maintain the bots
- Business sponsors: Leaders who champion the automation initiative
5. Start Small, Then Scale
Begin with a pilot project to demonstrate value and learn from the experience. Once you’ve proven success, gradually expand your automation program, building on lessons learned.
6. Establish Governance and Maintenance
Develop clear governance procedures for:
- Prioritizing automation opportunities
- Managing bot credentials and access
- Handling exceptions and errors
- Maintaining bots when underlying systems change
- Measuring and reporting on results
7. Communicate and Manage Change
Address employee concerns about automation by clearly communicating how RPA will impact roles and responsibilities. Focus on how automation will eliminate tedious tasks and allow for more valuable work, not replace jobs entirely.
The Future of RPA: Where Is It Heading?
RPA technology continues to evolve rapidly. Here are the trends shaping its future:
Intelligent Automation
The integration of RPA with AI capabilities is creating smarter automation solutions that can handle more complex processes. This includes:
- Cognitive automation: Adding reasoning capabilities to RPA
- Natural language understanding: Enabling bots to interpret unstructured text
- Machine learning: Allowing bots to improve through experience
Hyperautomation
Gartner coined this term to describe the approach of automating as many business processes as possible using a combination of technologies:
- RPA for task automation
- Process mining to discover automation opportunities
- AI for intelligent decision-making
- Low-code platforms for rapid development
- Integration platforms to connect systems
Cloud-Based RPA
Cloud RPA platforms offer greater scalability, accessibility, and lower infrastructure costs. This trend is making RPA more accessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
Citizen Developers
Low-code and no-code RPA tools are enabling business users without programming skills to create their own automation solutions, democratizing access to the technology.
RPA-as-a-Service
Subscription-based RPA offerings are emerging, allowing companies to access automation capabilities without large upfront investments.
Human-Bot Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, the future of work involves closer collaboration between people and digital assistants, with each focusing on what they do best.
Easy Steps to Start with RPA
If you’re interested in exploring RPA for your organization, here are some concrete steps to get started:
1. Educate Your Team
Ensure key stakeholders understand what RPA is and isn’t. Share case studies from your industry to illustrate potential benefits.
2. Identify Automation Candidates
Conduct a process inventory and evaluation to identify suitable candidates for automation. Look for processes that are:
- Manual and repetitive
- Rule-based
- High-volume
- Error-prone
- Time-consuming
3. Calculate Potential ROI
Develop a business case for RPA by estimating costs and benefits:
- Implementation costs (software, development, training)
- Ongoing costs (maintenance, licenses)
- Expected benefits (time savings, error reduction, improved compliance)
4. Select a Pilot Process
Choose a process for your initial implementation that is:
- Important enough to demonstrate value
- Simple enough to ensure success
- Visible enough to build momentum for your program
5. Explore RPA Tools
Most RPA vendors offer free trials or community editions of their software. Download these to get hands-on experience with the technology before making significant investments.
6. Develop Implementation Roadmap
Create a phased plan for implementing RPA across your organization, starting with quick wins and gradually tackling more complex processes.
Common Questions About RPA
What problems does RPA solve?
RPA addresses several business challenges:
- Manual, repetitive tasks that consume valuable employee time
- Data entry errors and inconsistencies
- Slow processing times for routine transactions
- Compliance risks due to human oversight
- Difficulty scaling operations during peak periods
- Integration challenges between legacy and modern systems
How is RPA different from traditional automation?
Unlike traditional automation that often requires API integration and programming, RPA works through the user interface just like a human would. This makes it:
- Faster to implement
- Less invasive to existing systems
- More flexible to changes
- Accessible to business users, not just IT
Will RPA replace human workers?
Rather than wholesale replacement, RPA typically changes the nature of jobs by:
- Eliminating repetitive, low-value tasks
- Allowing employees to focus on higher-value work
- Creating new roles in automation development and management
- Improving job satisfaction by removing mundane aspects of work
According to research by Forrester, while some jobs will be eliminated, many more will be enhanced and new roles will be created in the “automation economy.”
How long does it take to implement RPA?
Implementation timelines vary based on process complexity:
- Simple processes: 2-4 weeks
- Moderate complexity: 1-3 months
- Complex, cross-functional processes: 3-6 months or more
The good news is that unlike many IT projects, RPA can often deliver value in weeks rather than months or years.
How much does RPA cost?
RPA costs include:
- Software licenses: Typically $5,000-$15,000 per bot annually
- Implementation: Development costs vary widely based on complexity
- Infrastructure: Servers and environment setup
- Support and maintenance: Ongoing costs to maintain bots
Many organizations achieve positive ROI within 6-12 months for well-chosen automation projects.
Conclusion: Is RPA Right for Your Business?
Robotic Process Automation represents a significant opportunity for businesses of all sizes to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and free employees from repetitive tasks. As with any technology investment, success depends on thoughtful implementation focused on solving real business problems.
RPA isn’t a magic solution, but when applied to the right processes with proper planning and governance, it can deliver impressive results. The most successful organizations view RPA not just as a cost-cutting tool but as a way to enhance customer and employee experiences.
As you consider your automation journey, remember that it’s not about replacing humans with robots, but about creating a digital workforce that handles the routine so your human workforce can focus on what people do best: solving complex problems, building relationships, and innovating for the future.
Ready to explore how RPA might transform your business operations? Start by identifying those rule-based, repetitive processes that consume valuable time, and imagine what your team could accomplish if those tasks were handled automatically.
Want to learn more about how AI and automation can transform your business? Check out our related articles:
- What Is AI Automation? Real-World Benefits
- AI in Business: How It Works
- Understanding AI Task Automation
- How AI Saves Time for Teams
At Erudience, we specialize in AI automation solutions that help businesses streamline operations and improve customer experiences. Whether you’re looking to implement RPA or explore other AI technologies, our team can help you identify opportunities and develop a tailored automation strategy. Contact us to learn more about our services.
More Frequently Asked Questions About RPA
What does RPA mean?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation, which is technology that uses software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that humans typically perform.
What is the purpose of RPA?
The main purpose of RPA is to increase efficiency, reduce errors, and free up human workers from repetitive tasks so they can focus on more valuable activities that require creativity, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills.
How is RPA different from AI?
RPA follows specific rules to complete tasks, while AI can learn, adapt, and make decisions. RPA is best for structured, repetitive tasks, while AI handles unstructured data and complex situations. Many modern solutions combine both technologies.
What industries use RPA?
RPA is used across virtually all industries, including banking, healthcare, insurance, retail, manufacturing, telecommunications, energy, and the public sector. Any industry with repetitive, rule-based processes can benefit from RPA.
What are the key features of RPA?
Key features of RPA include: non-invasive integration with existing systems, visual process designers, scheduling capabilities, automated handling of structured data, and comprehensive audit logs of all activities performed.
What type of processes are good for RPA?
The best processes for RPA are rule-based, repetitive, digital tasks that involve structured data, have a high volume, low exception rate, and remain relatively stable over time.
What is the future of RPA?
The future of RPA includes greater integration with AI technologies, expansion into more complex processes, more accessible tools through low-code/no-code platforms, and cloud-based deployment options that make RPA accessible to organizations of all sizes.

